HCIE-路由交换 考试大纲
HCIE-Routing & Switching考试概况
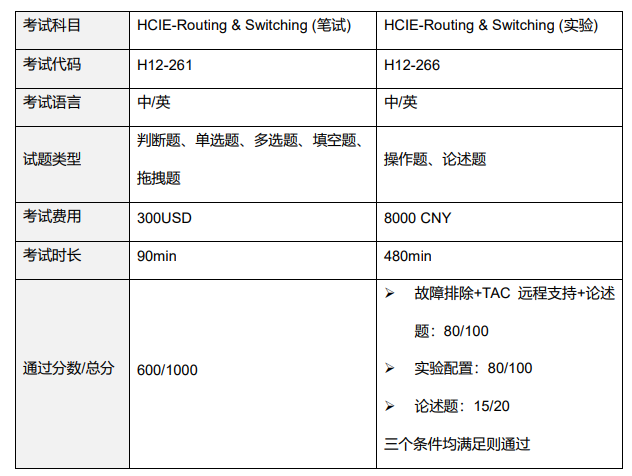
HCIE-Routing & Switching考试内容
HCIE-Routing & Switching V3.0 考试覆盖对企业网络的规划、设计、实施、维护、排障、 优化、割接等。
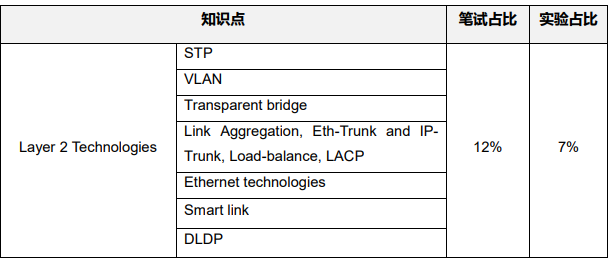
笔试知识点
一、Layer 2 Technologies
➽ STP
1. STP
2. RSTP
3. MSTP
4. Loop guard
5. Root guard
6. BPDU guard
7. TC-BPDU attack guard
➽ VLAN
1. Access port
2. Trunk port
3. Hybrid port
4. QinQ
5. Vlan Aggregation
6. Mux VLAN
7. Voice VLAN
➽ Transparent bridge
1. Local Bridging
2. Remote Bridging
3. Integrated Bridging and Routing
4. VLAN ID Transparent Transmission
➽ Link Aggregation, Eth-Trunk and IP-Trunk, Load-balance, LACP
1.Link Aggregation
2.LACP
➽ Ethernet technologies
1. Speed and duplex
2. Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, 10GE, 40GE,100GE
3. Auto MDI/MDIX
4. Auto negotiation
5. Storm control
6. Unicast flooding control
➽ Smart link
➽ DLDP
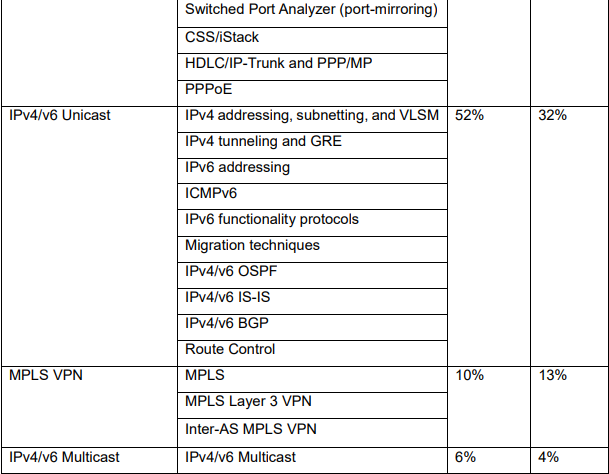
➽ Switched Port Analyzer (port-mirroring)
➽ CSS/iStack
➽ HDLC/IP-Trunk and PPP/MP
➽ PPPoE
二、IPv4/v6 Unicast
➽ IPv4 addressing, subnetting, and VLSM
➽ IPv4 tunneling and GRE
➽ IPv6 addressing
➽ ICMPv6
➽ IPv6 functionality protocols
➽ Migration techniques
1. Tunnelling techniques
2. Translation techniques
➽ IPv4/v6 OSPF
1. Standard OSPF areas
2. Stub area
3. Totally stubby area
4. NSSA
5. Totally NSSA
6. LSA types
7. Adjacency on a point-to-point and on a multi-access network
8. Virtual-Link
9. LSA Filter
10. OSPF Fast Convergence
11. Stub Router
12. OSPF Authentication
➽ IPv4/v6 IS-IS
1. NSAP
2. IS-IS Link-state packets
3. IS-IS area type
4. IS-IS circuit type
5. IS-IS TLV
6. IS-IS DIS and Pseudo node
7. IS-IS SPF
8. IS-IS LSP
9. IS-IS Metric
10. IS-IS Route Leaking
11. IS-IS MT
12. IS-IS Fast Convergence
13. IS-IS LDP Synchronization
14. IS-IS Authentication
➽ IPv4/v6 BGP
1. IBGP and EBGP
2. BGP attributes
3. BGP synchronization
4. BGP routes Summarization
5. Route Dampening
6. BGP route reflector
7. BGP Community
8. BGP Peer Groups
9. BGP Security
10. Principles of Route Selection
➽ Route Control
1. Filtering
2. IP Prefix list
3. Route Import(redistribution)
4. Route policy
5. Summarization
6. Preference
7. Other advanced features
三、MPLS VPN
➽ MPLS
1. MPLS network component (P, PE, CE)
2. MPLS label format
3. MPLS label encapsulation
4. MPLS label stack
5. MPLS label operation
6. Forwarding Equivalence Class
7. LDP
8. Label advisement model
9. MPLS LDP—Local Label Allocation Filtering
10. MPLS LDP Inbound/outbound Label Binding Filtering
➽ MPLS Layer 3 VPN
1. MP-IBGP VPNv4 peering
2. VPN-instance
3. Route Distinguisher
4. Route Target
5. Route Target import/export
6. PE-CE–Dynamic Routes
7. PE-CE–Static Routes
8. Redistributing PE-CE routes into VPNv4
9. Redistributing VPNv4 routes into PE-CE routing table
10. MCE
➽ Inter-AS MPLS VPN
Option A、Option B、Option C
四、IPv4/v6 Multicast
1. Multicast distribution tree
2. Multicast forwarding
3. Multicast RPF
4. PIM sparse mode
5. IGMP/MLD
6. IGMP Snooping/MLD Snooping
7. PIM RP, and BSR
8. Multicast tools, features, and source-specific multicast
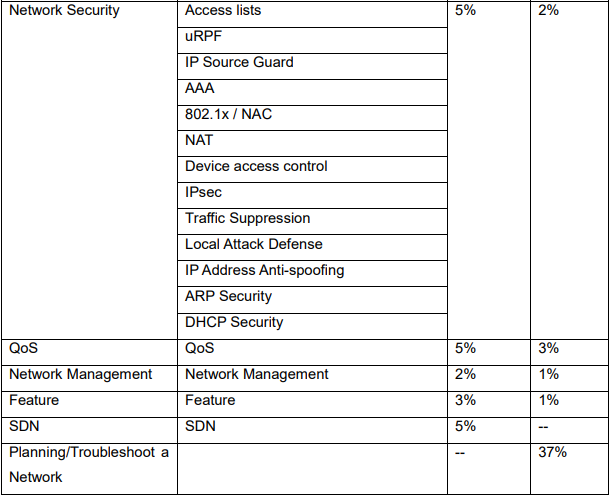
五、Network Security
➽ Access lists
➽ uRPF
➽ IP Source Guard
➽ AAA
➽ 802.1x / NAC
➽ NAT
1. Static NAT/NAPT
2. Dynamic NAT/PAT
3. Easy IP
4. NAT Server
5. Twice NAT
6. ALG
7. NAT Mapping
8. NAT Filtering
➽ Device access control
➽ IPsec
➽ Traffic Suppression
➽ Local Attack Defense
➽ IP Address Anti-spoofing
➽ ARP Security
➽ DHCP Security
六、QoS
1. Classification
2. Traffic Policing
3. Traffic Shaping
4. Congestion Avoidance
5. Congestion Management
七、Network Management
1. Syslog
2. IP Service Level Agreement SLA
3. NetStream
4. NQA
5. SNMP
6. FTP
7. Telnet
8. SSH
八、Feature
1. VRRP
2. VGMP
3. Interface Backup
4. NTP
5. DHCP
6. BFD
7. NSF/GR
8. NSR
九、SDN
1. Strategy of SDN/NFV
2. SDN architecture
3. VXLAN
4. EVPN
实验知识点
一、Layer 2 Technologies
➽ STP
1.STP
2. RSTP
3. MSTP
4. Loop guard
5. Root guard
6. BPDU guard
7. TC-BPDU attack guard
➽ VLAN
1. Access port
2. Trunk port
3. Hybrid port
4. QinQ
5. Vlan Aggregation
6. Mux VLAN
7. Voice VLAN
➽ Transparent bridge
1. Local Bridging
2. Remote Bridging
3. Integrated Bridging and Routing
4. VLAN ID Transparent Transmission
➽ Link Aggregation, Eth-Trunk and IP-Trunk, Load-balance, LACP
1. Link Aggregation
2. LACP
➽ Ethernet technologies
1. Speed and duplex
2. Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, 10GE, 40GE, 100GE
3. Auto MDI/MDIX
4. Auto negotiation
5. Storm control
6. Unicast flooding control
➽ Smart link
➽ DLDP
➽ Switched Port Analyzer (port-mirroring)
➽ CSS/iStack
➽ HDLC/IP-Trunk and PPP/MP
➽ PPPoE
二、IPv4/v6 Unicast
➽ IPv4 addressing, subnet, and VLSM
➽ IPv4 tunneling and GRE
➽ IPv6 addressing
➽ ICMPv6
➽ IPv6 functionality protocols
➽ Migration techniques
1. Tunnelling techniques
2. Translation techniques
➽ IPv4/v6 OSPF
1. Standard OSPF areas
2. Stub area
3. Totally stubby area
4. NSSA
5. Totally NSSA
6. LSA types
7. Adjacency on a point-to-point and on a multi-access network
8. Virtual-Link
9. LSA Filter
10. OSPF Fast Convergence
11. Stub Router
12. OSPF Authentication
➽ IPv4/v6 IS-IS
1. NSAP
2. IS-IS Link-state packets
3. IS-IS area type
4. IS-IS circuit type
5. IS-IS TLV
6. IS-IS DIS and Pseudo node
7. IS-IS SPF
8. IS-IS LSP
9. IS-IS Metric
10. IS-IS Route Leaking
11. IS-IS MT
12. IS-IS Fast Convergence
13. IS-IS LDP Synchronization
14. IS-IS Authentication
➽ IPv4/v6 BGP
1. IBGP and EBGP
2. BGP attributes
3. BGP synchronization
4. BGP routes Summarization
5. Route Dampening
6. BGP route reflector
7. BGP Community
8. BGP Peer Groups
9. BGP Security
10. Principles of Route Selection
➽ Route Control
1. Filtering
2. IP Prefix list
3. Route Import(redistribution)
4. Route policy
5. Summarization
6. Preference
7. Other advanced features
三、MPLS VPN
➽ MPLS
1. MPLS network component (P, PE, CE)
2. MPLS label format
3. MPLS label encapsulation
4. MPLS label stack
5. MPLS label operation
6. Forwarding Equivalence Class
7. LDP
8. Label advisement model
9. MPLS LDP—Local Label Allocation Filtering
10. MPLS LDP Inbound/outbound Label Binding Filtering
➽ MPLS Layer 3 VPN
1. MP-IBGP VPNv4 peering
2. VPN-instance
3. Route Distinguisher
4. Route Target
5. Route Target import/export
6. PE-CE–Dynamic Routes
7. PE-CE–Static Routes
8. Redistributing PE-CE routes into VPNv4
9. Redistributing VPNv4 routes into PE-CE routing table
10. MCE
➽ Inter-AS MPLS VPN
Option A、Option B、Option C
四、IPv4/v6 Multicast
1. Multicast distribution tree
2. Multicast forwarding
3. Multicast RPF
4. PIM sparse mode
5. IGMP/MLD
6. IGMP Snooping/MLD Snooping
7. PIM RP, and BSR
8. Multicast tools, features, and source-specific multicast
五、Network Security
➽ Access lists
➽ uRPF
➽ IP Source Guard
➽ AAA
➽ 802.1x / NAC
➽ NAT
1. Static NAT/NAPT
2. Dynamic NAT/PAT
3. Easy IP
4. NAT Server
5. Twice NAT
6. ALG
7. NAT Mapping
8. NAT Filtering
➽ Device access control
➽ IPsec
➽ Traffic Suppression
➽ Local Attack Defense
➽ IP Address Anti-spoofing
➽ ARP Security
➽ DHCP Security
六、QoS
1. Classification
2. Traffic Policing
3. Traffic Shaping
4. Congestion Avoidance
5. Congestion Management
七、Network Management
1. Syslog
2. IP Service Level Agreement SLA
3. NetStream
4. NQA
5. SNMP
6. FTP
7. Telnet
8. SSH
八、Feature
1. VRRP
2. VGMP
3. Interface Backup
4. NTP
5. DHCP
6. BFD
7. NSF/GR
8. NSR
九、Planning/Troubleshoot a Network
1. Planning/Troubleshoot complex Layer 2 network
2. Planning/Troubleshoot complex Layer 3 network
3. Planning/Troubleshoot a network in response to application
4. Planning/Troubleshoot network services
5. Planning/Troubleshoot network security
请注意: 该考试大纲是对考生在拥有多年实际工作经验的前提下进行备考时的补充,不代表 HCIE- Routing & Switching V3.0 考试中不能考查其他知识。该考试大纲代表了我们要求考生至少要掌 握的知识,考生必须能够熟练应用这些知识和相关知识点,才能通过 HCIE- Routing & Switching V3.0 的考核。

上一篇: HCIE-Datacom 考试大纲
下一篇: 最后一篇





 闽公网安备 35012102500533号
闽公网安备 35012102500533号